Niacinamide, a form of vitamin B3, is a widely used skincare ingredient praised for its versatility. Below is an evidence-based guide to its key actions, how it fits into routines, and what to expect.
Table of Contents
What it does?

This Serum Supports skin barrier function by increasing ceramide and fatty acid production, which helps retain moisture and protect against irritants.
Anti-inflammatory effects can help calm redness and reduce the appearance of blemishes.
Modulates sebum production, which can benefit oily and acne-prone skin.
Improves uneven skin texture and reduces the appearance of fine lines over time.
Anti-oxidant properties may help counter environmental stressors.
Concentration guidelines

| Niacinamide % | Best For | Benefits | Irritation Risk |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2–3% | Beginners, sensitive skin | Hydration, barrier support | Very low |
| 5% | Normal, combo skin | Texture smoothing, oil control | Low |
| 10% | Oily & acne-prone skin | Strong oil regulation, redness reduction | Moderate |
| 10%+ | Targeted use only | Aggressive effects | Higher, may irritate |
Ingredient compatibility and what to avoid
- Works well with:
- Humectants like glycerin and hyaluronic acid (for hydration).
- Ceramides and fatty acids (to support the skin barrier).
- Non-irritating sunscreens and antioxidants.
- Be cautious with or test first:
- Very high concentrations of AHAs/BHAs when used concurrently, as this can irritate sensitive skin. If you use acids, consider applying niacinamide in a different routine time (AM vs PM) or on alternate days at first.
- Unrelated strong irritants (fragrances, essential oils) should be muted when you’re first integrating niacinamide.
- Sensitive skin tip: If you’re reactive, consider formulas labeled for sensitive skin or products with soothing excipients like panthenol (pro-Vitamin B5) or allantoin along with niacinamide, and patch-test first.
What the product can improve
- Skin barrier resilience
- Hydration and plumpness
- Inflammation and redness control
- Texture and smoothness
- Occasional blemish control and reduced pore visibility
If you struggle with dryness during colder months, don’t miss my complete guide on winter skincare essentials to keep your barrier protected and hydrated.
How skin feels after use
- Often feels hydrated and comfortable, sometimes with a slight cooling or tingly sensation if your skin is new to active ingredients.
- Generally lightweight and non-greasy in most water-based formulations.
- Should not cause heavy residue; absorbs relatively quickly in typical serums or moisturizers.
Want products that won’t melt off in the heat? Check my article on summer skincare for fresh, shine-free skin.
-
Eczema-Friendly Skincare: Brands, Shopping Tips, and Safe Solutions
overview: what you’ll get from this guide Best over-the-counter creams for eczema relief About 10–20% of … Eczema-Friendly Skincare: Brands, Shopping Tips, and Safe SolutionsRead more
-
Machine Learning 2026: Skyrocket Your Career with Revolutionary AI Mastery
Key Takeaway Essential Machine Learning Skills and Prerequisites for 2025 Which programming languages can boost your … Machine Learning 2026: Skyrocket Your Career with Revolutionary AI MasteryRead more
-
Contact us
We’d love to hear from you! If you have any questions, feedback, suggestions, or business inquiries, … Contact usRead more
Expected results and timeline
- First 2–4 weeks: Improved hydration, minor reduction in redness or irritation for sensitive or reactive skin; beginning support for barrier function.
- 4–8 weeks: Noticeable improvements in skin texture, refinement of pores, and more even tone for many users.
- 8–12+ weeks: More sustained barrier support, ongoing improvement in dullness and uneven tone for some individuals.
Note: Individual timelines vary based on concentration, formulation, skin type, and consistency of use. For glowing, glass-skin results, don’t miss my guide on K-beauty ingredients and how to use them.
Suitable skin types
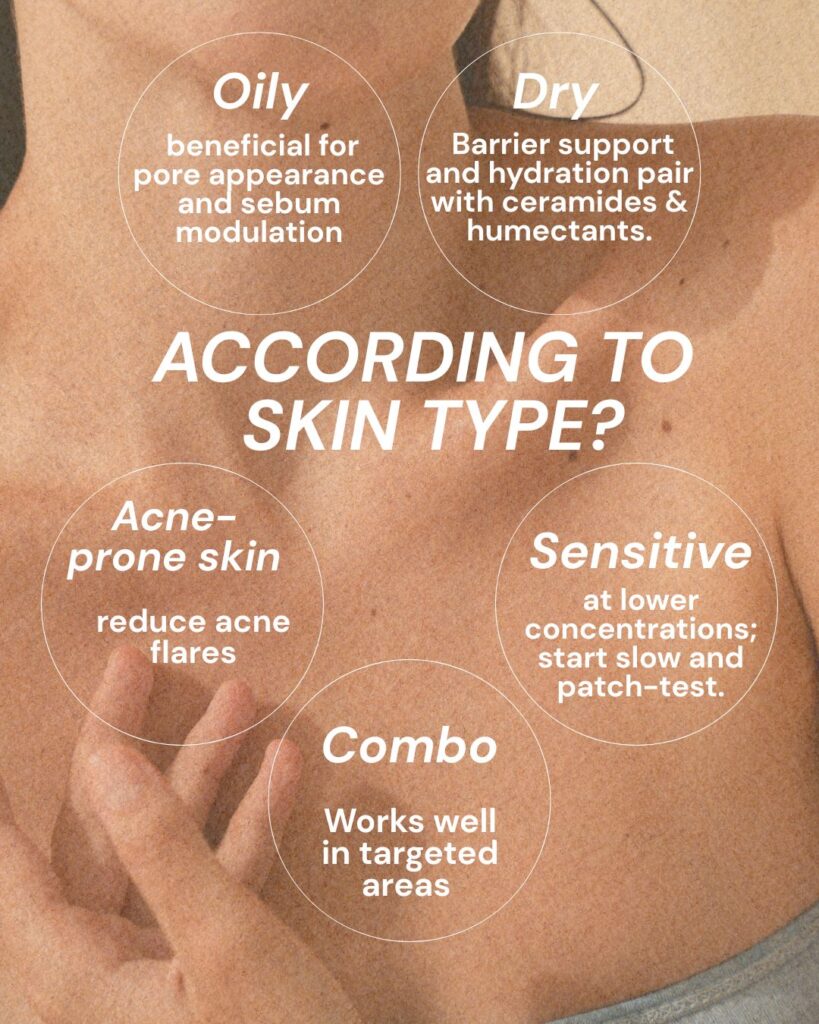
Numerous studies have highlighted the wide-ranging effects of niacinamide on human skin, from improving barrier function to reducing pigmentation. Read a detailed scientific review here.
Alternatives for sensitive-skin users (natural/gentle options)
If you have highly sensitive or reactive skin and prefer natural-bases or gentler options, consider:
- Products labeled for sensitive skin with soothing bases (e.g., oat extract, allantoin, chamomile) alongside a mild niacinamide option at lower concentrations after patch testing.
- Alternatives that support barrier health with low irritation risk, such as ceramide-rich moisturizers that may include soothing botanical extracts.
- Always patch-test any new product for 24–72 hours on a small area.
Important: While natural ingredients can be soothing, they can also cause allergies. Check ingredients lists and perform a patch test before full use. Looking to boost your energy naturally? Visit my post on Holistic Living Made Easy.
How to apply
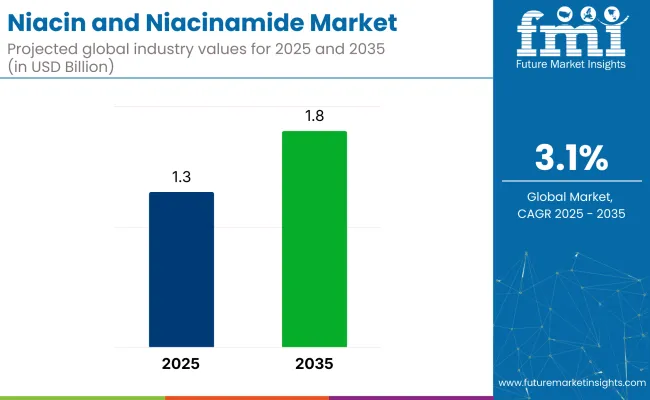
This graph shows the growing market of niacinamide from 2025- 35.
- Step-by-step:
- Cleanse your face with a gentle cleanser.
- If using toner or hydrating serum, apply that first.
- Apply a moisturizer afterward to lock in moisture.
- Finish with sunscreen in the daytime.
- How often:
- Start with once daily, preferably in the evening to reduce potential sun sensitivity.
- If well-tolerated after 1–2 weeks, you can increase to twice daily (AM and PM) or maintain at once daily depending on your skin’s tolerance and the product’s instructions.
- AM or PM:
- PM is a common starting point; you can use in the morning if your product is paired with sunscreen and non-irritating ingredients.
- Layering with other products:
- After cleansing, apply hydrating products (humectants) first.
- Follow with niacinamide serum or product.
- Apply a moisturizer to seal in hydration.
- Use sunscreen as the final step in the morning.
- If using acids (AHAs/BHAs) or retinoids, consider alternating days or applying niacinamide at a different time to minimize irritation.
- If layering with acids or retinoids:
- Morning: cleanser, hydrating serum, niacinamide, moisturizer, sunscreen.
- Evening: cleanser, acid/retinoid (as directed), niacinamide (if tolerated), moisturizer.
- Always monitor skin response and adjust.
Explore how AI is reshaping physical health, from smart wearables to predictive injury prevention, helping individuals improve fitness, mobility, and everyday wellbeing.
Practical tips and cautions
- Patch-test new products containing niacinamide for 24–72 hours on a small skin area.
- If irritation occurs (redness, burning, itching), reduce frequency or concentration or discontinue use.
- Store products away from heat and light to maintain stability.
At the end of your blog, you can have a Further Reading section: Web med
💬: Which skin concern do you struggle with the most—redness, oiliness, or texture? Tell me below so I can create content for you.
1. Why does niacinamide sometimes cause flushing or temporary redness?
Though rare, niacinamide can convert into nicotinic acid if the product is unstable or exposed to high heat. This can cause mild, temporary flushing. Choosing well-formulated and properly stored products significantly reduces this risk.
2. How does niacinamide strengthen the skin barrier on a biochemical level?
Niacinamide increases the synthesis of ceramides, free fatty acids, and cholesterol—the essential lipids that form the skin’s protective barrier. This improves the stratum corneum’s lipid matrix, reducing transepidermal water loss (TEWL) and enhancing hydration and resilience.
3. Does niacinamide influence melanin production, and can it treat deeper hyperpigmentation?
Yes—niacinamide inhibits the transfer of melanin from melanocytes to keratinocytes. While it effectively improves mild to moderate hyperpigmentation, deeper dermal pigmentation (like melasma) may require combination therapy with treatments such as tranexamic acid, azelaic acid, or professional procedures for optimal results.



